Theme: Novel Insights in Molecular Medicine and Diagnosis for Leading a Better Life
Molecular Medicine 2019
- About Conference
- Scientific Sessions
- Market Analysis Report
- New Updates on Molecular Medicine and Diagnostics
Molecular Medicine 2019
Conference Information here :
ME Conferences is pleased to announce the upcoming “4th International Conference on Molecular Medicine and Diagnostics” during July 15-16, 2019 in Abu Dhabi, UAE.
Molecular Medicine 2019 focuses on sharing of scientific knowledge and experience in all areas applied to Molecular Medicine, Diagnostics and related scientific fields. It provides the platform for researchers, scientists, and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, concerns, practical challenges encountered, and solutions adopted in the fields of Molecular Medicine and Diagnostics. Our conference is oriented to shape future research directions by driving the scientific community at large by facilitating access to the newest technical and scientific achievements.
The 2019 Molecular Medicine Conference is bringing together 50+ professionals from 9+ countries for education, innovation, and collaboration. Choose from 20+ education sessions, many of special sessions and endless networking events.
Abstracts are welcome in all areas related to Molecular Medicine and Diagnostics.
Registration: MMC19 registration is now open. View registration pricing
Conference Benefits :
- Globally providing opportunities - Professional development for fellows and students in this field.
- Get up-to-date information on Molecular Medicine trends.
- Learn best practices that you can adapt to.
- Explore new and emerging technologies.
- Share new challenges and solutions within your professional community.
- Learn about new products and services in your field to increase your productivity.
- Connects professionals across the world to discuss new developments.
- Generating insights beyond boundaries.
- CPD accreditation: Molecular Medicine 2019 has been accredited by the Continuing Professional Development (CPD).
Target Audience :
- Molecular Biologists
- Molecular Diagnostic Companies
- Molecular Pathologists
- Molecular Geneticists
- Molecular Oncologists
- Biotechnologists
- Bioinformaticians
- Clinicians
- Clinical Chemists
- Pharmacogenetist
- Genome surgeons
- Geneticists
- Immunologists
- Stem cell Developers & Researchers
- Students
- Research Scholars
- Scientists
- Pharma and biotech companies
- Health care industries
- Business Entrepreneurs
Sessions / Highlights in Molecular Medicine 2019
Track 1: Molecular Medicine
Molecular medicine is a broad field which deals with the development of diseases at a molecular level and identifies fundamental molecular and genetic errors of disease and to develop molecular interventions to correct them. Molecular structures and mechanisms are described by Physical, chemical, biological, bioinformatics and medical techniques. Disease pathogenesis at the molecular or physiological level may lead to the design of specific tools for disease diagnosis, treatment, or prevention.
By understanding the genes, proteins, and other cellular molecules work molecular medicine develops ways to diagnose and treat disease. Molecular Medicine develops knowledge and skills in cellular and molecular biology.
-
Molecular Medicine Cancer
-
Molecular Medicine Scope
-
Molecular Mechanisms
-
Molecular Surgery
-
Metabolomics
-
Molecular pathological epidemiology
Track 2: Molecular Diagnostics
Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyse an individual's genetic code and to identify biological markers in the genome and proteome. Molecular diagnostics apply molecular biology to see how cell express their genes to medical testing. For any successful application of gene therapy or biologic response modifiers, molecular diagnostics offers a great tool. Molecular diagnostics now provides most laboratory tests in infectious diseases, genetics, and an increasing number in oncology. Molecular diagnostics analyse a person's health at a molecular level by detecting specific sequences in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA) that may be related to disease
-
Genetic Tests
-
Molecular Tests
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction
-
Molecular Diagnostics Market
-
Molecular Biology
-
Medical Testing
-
Genetic hybridization tests
Track 3: Molecular Genetics and Genomics
Molecular genetics employs methods of both molecular biology and genetics to study the structure, function and interactions among genes at a molecular level.
The study of chromosomes and gene expression of an organism can give an accurate and deep understanding of heredity, genetic variation, and mutations. Molecular Genetics and Genomics cover all areas on the latest research innovations, population genetics, gene function and expression and molecular genetics. Molecular genetics is concerned with the study of your favourite gene, genomics is concerned with studying all the genes. Molecular genomics is a critical component of the expanding database linking alterations of DNA and RNA with the disease, disease prognosis and therapeutic response.
-
Genes and genomes
-
PCR and Real-Time PCR
-
Microarrays
-
Next-Generation Sequencing
-
Sanger Sequencing
Track 4: Molecular Oncology
Molecular oncology refers to the chemistry of cancer and tumours at the molecular scale and their development and application on molecularly targeted therapies.
Molecular Oncology studies especially the genetic alterations and their implications. Molecular Oncology focuses on new discoveries, approaches, as well as technical developments in basic, clinical and discovery-driven cancer research. It mainly focuses on advances in the understanding of disease processes leading to human tumour development. Molecular Oncology establishes novel concepts of clear clinical significance in diagnosis, prognosis and prevention strategies.
-
DNA repair
-
Apoptosis
-
Cancer genetics
-
Molecular pathology
-
Tumour immunology
Track 5: Molecular Biomarkers and Diagnosis
A biomarker is used as an indicator of the biological state. In routine clinical use Oncology biomarkers actually, make their way. A biological marker points to the presence of a disease, a physiological change, response to treatment, or a psychological condition.
Molecular biomarkers are used for various purposes including disease diagnosis and prognosis and assessment of treatment response. Over the last decade, there has been a significant increase in the number of drug labels containing information on molecular biomarkers. In most of the chronic diseases, biomarkers can confirm a difficult diagnosis or even make it possible in the first place.
-
Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers
-
Drug labelling
-
Cancer biomarkers
-
Disease-related biomarkers
-
Drug-related biomarkers
-
Biomarkers in Drug Development
-
Biomarker requirements
Track 6: Cellular and Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the study of biological activity between biomolecules in the various systems of a cell. It also includes the interactions between DNA, RNA, proteins and their biosynthesis as well as the regulation of these interactions.
Cellular and Molecular Biology majorly study the processes that occur within and between the body's cells. This includes genes, the way cells carry nutrients throughout the body, and how diseases attack healthy cells. The process of replication, transcription and translation of the genetic material are studied under Molecular biology. Cellular biology study cells, including their function, systems, structure and interactions with living organisms. These typically work in medical fields and are often focused on the treatment of disease.
-
Genetics
-
Biochemistry
-
Immunology
-
Cytochemistry
-
Cell signalling
-
Transcription
-
Structural biology
Track 7: Molecular Pathology
Molecular pathology is the study of molecules within organs, tissues or bodily fluids. Molecular pathology is commonly used in the diagnosis of bone, soft tissue tumours, cancer and infectious diseases. The purpose of molecular pathology is to understand the mechanisms of disease by identifying molecular and pathway alterations. It is considered the heart of modern diagnostics and translational research. Molecular pathology studies and diagnose disease through the examination of genetic and molecular abnormalities. Molecular pathology and biomarkers are used to study molecular and genomic abnormalities in tissues for diagnostic and prognostic purposes. Molecular diagnosis is useful and sometimes necessary as an adjunct for diagnosis especially in morphologically or clinically unusual lesions.
-
Molecular diagnostics
-
Molecular Genetic Pathology
-
Medical Genetics
-
Molecular tests
-
Molecular pathological epidemiology
-
Pathology
-
Precision medicine
Track 8: Molecular Evolution
Living things all are alike at the cellular and molecular level. The fundamental similarities between living organisms are explained by evolutionary theory. Major topics in molecular evolution concern the rates and impacts of single nucleotide changes, origins of new genes, the evolution of development, and ways that evolutionary forces influence genomic and phenotypic changes. Some of the key advances are quantitative estimates of both the diversity in populations and of evolutionary relationships, as well as improvements in theoretical understanding. There is an improved understanding of the function of proteins and much better models of the common patterns of development.
-
Mechanisms of molecular evolution
-
Evolutionary biology
-
Population genetics
-
Mutation
-
Genetic drift
-
Gene content and distribution
-
Molecular phylogenetics
Track 9: Advances in Molecular Diagnostics
Advances in cell and molecular biology studies have revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of many different diseases. It is considered as a modern Biotechnology concerned with understanding the Genetic Diagnosis, Molecular Diagnosis, Molecular Forensics.
People at the present day are facing serious global challenges in healthcare from emerging and re-emerging diseases. The availability of new sequencing methods, microarrays, microfluidics, biosensors, and biomarker assays has made a shift toward developing diagnostic platforms, which stimulates growth in the field regarding diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment, leading to improved outcomes and greater cost savings.
-
Genetic Marker
-
Screening
-
DNA-Profiling
-
Cytogenetics
-
Transcriptome
-
Cancer Biomarkers
-
Biomarker Toxicologies
-
Inherited Diseases
Track 10: Prenatal Molecular Diagnostics
Much research is being done in foetal whole exome sequencing and is beginning to play a large role in miscarriage testing. With all this research and screening, clinicians and genetic counsellors need to keep abreast of these changes and guidelines in order to effectively care for patients.
The genetic cause of foetal abnormalities detected on ultrasound imaging and in high-risk families can be significantly identified and improved in Foetal diagnostic exome sequencing. Testing based on isolation of foetal cells from maternal blood would provide an attractive alternative to testing of cell-free DNA. An updated implementation of these different approaches will make lively discussion and insight into this field and is headed ways for researchers, test providers, clinicians and clinics to take these developments into consideration.
-
Advances in Prenatal Molecular Diagnostics
-
Cell-free DNA screening
-
Cell-based DNA testing
-
Biomarkers for preeclampsia and pre-term birth
-
Prenatal and Reproductive Diagnostics
-
Non-Invasive Prenatal Diagnosis
Track 11: Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Point-of-care testing is medical diagnostic testing at the time and place of patient care. In Recent years there are tremendous advances in POCD due to innovations lab-on-a-chip technologies, and complementary technologies. Critical advances in POCD provides directions for future research. Point-of-care allows physicians and medical staff to accurately achieve real-time, lab-quality diagnostic results within minutes rather than hours. The global Point of Care diagnostic tests renders immediate results providing improved patient care in rural areas too. This factor has significantly impacted the market growth.
-
Point-of-Care Testing by Clinical Setting
-
Point-of-Care Testing Patents
-
Chronic Disease Management at the Point of Care
-
POC Informatics
-
Increasing Global Access to Care
-
Portable Point-Of-Care Testing Systems
Track 12: Clinical Diagnostics & Research
Clinical diagnostics is defined as diagnosis and treatment of human disease. Clinical diagnostics for a disease can be done by patient's complaints based on signs, symptoms and medical history rather than on laboratory examination or medical imaging. Clinical diagnostics is considered as an ever-changing field of medicine and research. In recent years Clinical diagnostics has become more exciting as advances in new techniques aid in fulfilling the potential of personalized medicine. Clinical research determines the safety and effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatments.
-
Differential diagnosis
-
Diagnostic Test
-
Nursing diagnosis
-
Clinical diagnosis of ADHD
-
Clinical research ethics
-
Clinical Trial Management System
-
Clinical Biostatistics
Track 13: Biosimilar Monoclonal Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb) is originally produced by a single B-cell. Biosimilars are a lot complicated than small-molecule medicine and generics. In the past few years, monoclonal antibody drugs have dominated the world's largest biopharmaceutical drug sales, and in the coming years, monoclonal antibody drugs will continue to be the main force. Considering the huge profit margins and potential market, the monoclonal antibody-based therapeutics is the hot territory many pharmaceutical companies chases. This session will summarize the market in terms of therapeutic applications, type, and structure of mAbs, dominant companies, manufacturing locations, and emerging markets. These requirements would lead to greater development in the process and tighter quality controls during the production of biosimilar mAbs.
-
FDA-approved mAb drugs
-
Monoclonal antibody therapy
-
Anti-Cancer Antibodies
-
Cancer Immune therapy
-
Antibody Humanization Technologies
-
Biotherapeutics : Early Analytical Development
Track 14: Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic organisms such as viruses, bacteria, or fungus. Normally harmless but under certain conditions, they can be fatal and can cause death too. They can be spread from one person to another directly or indirectly. Infectious diseases are caused by infection-causing organisms that use the human body for surviving, reproducing and colonizing. These organisms are known as pathogens.
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections;
Antiviral agents treat viral infections;
and
Antifungal agents treat fungal infections.
-
Urinary Tract Infections
-
Neurodegenerative Diseases
-
Cryptococcal meningitis
-
Bacterial Infectious Diseases
-
Viral Infectious Diseases
-
Protozoal Infectious Diseases
-
Fungal Infectious Diseases
-
Zoonotic diseases
Track 15: Next-Generation Sequencing
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionised the study of genomics and molecular biology by allowing us to sequence DNA and RNA much more quickly and cheaply than the previously used Sanger sequencing. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) relies on capillary electrophoresis. NGS although with shorter read lengths and less accuracy reduces the time that genome sequencing projects took with Sanger methods.
Thousands to millions of DNA molecules can be sequenced simultaneously by using Powerful Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) platform. By offering a high throughput option NGS is revolutionizing in fields such as personalized medicine, genetic diseases, and clinical diagnostics.
-
llumina (Solexa) sequencing
-
Roche 454 sequencing
-
Proton / PGM sequencing
-
SOLiD sequencing
-
Massive parallel sequencing
-
Sanger sequencing
Track 16: Immunogenicity Testing
Immunogenicity is the ability of a particular substance induce a humoral and/or cell-mediated immune responses. An immune response can be potentially elicited by administering any substance into the human body.
Products which increase the potential of anti-drug antibodies include :
Therapeutic antibodies, enzyme therapies, peptides and combination products.
An immune response may also impact a drug’s safety and efficacy. Assays should be designed in such a way that they provide sufficient sensitivity and are free from potential risks to the target patient population. By designing assays with these factors, it is possible to gather data about the strength and type of immune response that a drug may produce in humans.
-
Bridging ELISA
-
Type II hypersensitivity reaction
-
Clinical Trial Support
-
Total Antibody Assay
-
Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay (ELISA)
Track 17: Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered from environmental samples. Metagenomics could be an asset of analysis techniques comprising several connected approaches and ways. We tend to anticipate that metagenomics can complement and stimulate analysis on people and their genomes.
Metagenomics represents a brand-new approach in exceedingly genomic analysis. Metagenomic libraries can be screened for novel physiological, metabolic, and genetic options. Though long and labour-intensive, metagenomics is the most powerful environmental approach that provides prospects to get novel genes and novel biomolecules through the expression of genes from an uncultivated and unknown bacterium in a recipient host cell. Metagenomic information ought to contain DNA sequences for all the genes within the microorganism community
-
Application of Genomics to Uncultured Microorganisms
-
Gene analysis by metagenomics
-
The Human Microbiome
-
Microbial Metagenomics
-
Metatranscriptomics
-
Metaproteomics
Track 18: Stem Cell & Regeneration
Cell therapies and regenerative medication boost the health of patients by repairing, replacing, or by creating broken cells within the body. Some elements of our bodies will repair themselves quite well when injured, while others don’t repair in any respect. We can’t develop an entire leg or arm; however, some animals will develop – or regenerate – whole body elements. Stem cells (SC) offer totally different. Despite the promise of embryonic stem cells, in several cases, adult or perhaps vertebrate stem cells give a lot of fascinating approach for clinical applications. Clinical applications in regenerative medication have increased tremendously throughout the last ten years. Regenerative medication revolutionizes the method to improve the health and quality of life by restoring, maintaining or enhancing tissue and functions of organs.
-
Regenerative Medicine
-
Cord blood
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells
-
Stem cell treatments
-
Artificial organ
-
Cell therapies
-
Aesthetic medicine
Track 19: Clinical Chemistry
Clinical chemistry is usually involved with analysis of bodily fluids for diagnostic and therapeutic functions. It's an applied style of organic chemistry. There are currently several blood tests and clinical tests with intensive diagnostic capabilities. These are performed on any bodily fluid or plasma. The foremost common specimens tested in clinical chemistry are blood and Serum. Many various tests exist to check glucose, electrolytes, enzymes, hormones, lipids (fats), and proteins. By running tests on these samples, physicians will confirm patient conditions and potential diseases, and recommend a counselled treatment up. Clinical chemistry procedures create precise diagnoses, offer effective treatment choices and monitor a patient’s response to treatment.
-
Clinical Endocrinology
-
Toxicology
-
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
-
Urinalysis
-
Panel tests
-
Clinical Biochemistry
-
Blood Tests
Track 20: Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics is the study of the gene effect on a person’s response to medication. This comparatively new field combines pharmacological medicine and genetics to develop effective, safe medications and doses that may be tailored to a person’s genetic makeup. Several medications presently accessible do not work a similar manner for everybody. Adverse drug reactions are a unit of big trouble for hospitalizations. With the data gained from the HGP, researchers are learning variations in genes have an effect on the body’s response to medications.
The field of pharmacogenomics continues to be in its infancy. Its use is presently quite restricted, however new approaches are in clinical trials. In future, pharmacogenomics can permit the tailored medication to treat health issues, as well as disorders, Alzheimer sickness, cancer, HIV/AIDS, and asthma.
-
Drug-Gene Testing
-
Clinical Pharmacogenomics
-
Precision Pharmacotherapy
-
Pharmacogenetics
-
Personalized Medicine
-
Pharmacoproteomics
Track 21: DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the method of sequencing the base pairs of a DNA (As, Ts, Cs, and Gs). Sequencing a whole organism’s DNA is a huge task. It needs breaking the DNA into several smaller items, sequencing the items, and collection of these sequences into one long "consensus."
These bases give the information on genotype and also the phenotype. Nucleotides aren't the sole determinants of phenotypes but are essential to their information. Every individual and organism feature a specific ester base sequence. DNA sequencing additionally underpins pharmacogenomics. This can be a comparatively new field that is leading to an individualized medication. Over a hundred and forty medication approved by the FDA currently by pharmacogenomic data in their labelling.
-
DNA extraction
-
DNA polymerase
-
Epigenetics
-
Recombinant DNA
-
Restriction enzymes
-
Sanger sequencing
Track 22: Translational and Molecular Medicine
Translational medicine is defined as an interdisciplinary branch of the biomedical field. By using a highly collaborative approach Translational medicine is growing in biomedical research discipline and aims to expedite the discovery of new diagnostic tools and treatments. Within public health, translational medicine is focused on ensuring proven strategies for disease treatment and prevention. Translational medicine aims to improve human health and longevity by determining the relevance to human disease of novel discoveries in the biological sciences. Translational medicine is enhancing the efficiency of biomedical discovery and application. There are many compelling reasons to find cost-effective solutions to health care delivery.
-
Current Research in Translational Medicine
-
Clinical and Translational Medicine
-
Disease-targeted research
-
Evidence-based research
-
Preclinical research
-
Translational medical science
Track 23: Integrative Molecular Medicine
Integrative Molecular Medicine covers novel findings in molecular, biological, and biomedicine research. The broad spectrum of Integrative Molecular Medicine includes rare and common disorders from diagnosis to treatment.
Molecular drugs strive to know traditional body functioning and illness pathological process at the molecular level which can enable researchers and physician-scientists to use that information within the style of specific molecular tools for illness identification, treatment, and prognosis. Integrative Molecular drugs (imMed) offers a scientific setting, which mixes basic and clinical analysis and offers a broad vary of advanced opportunities.
-
Clinical Science
-
Integrative Molecular Biology & Biotechnology
-
Medical Microbiology
-
Nanotechnology
Market Growth of Molecular Medicine and Diagnostics
Market Growth of Molecular Medicine Research in the last and upcoming ten years :
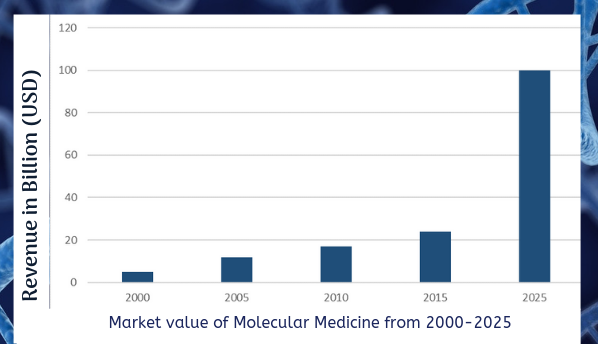
Medical doctors, patients, and health care providers consider the prevention of genetic diseases as an essential tool to improve the general health status of the population and the proportion of people suffering from genetics and genomics disease will increase by 65.2% by 2025. The top institutions researching in the related studies have been funded with 100 Billion Dollar worldwide. According to recent statistics, genetic diseases worldwide will double between 2012 and 2025. The market value of Molecular Medicine is $24 billion in 2015 and is expected to reach more than $100 billion by 2025.
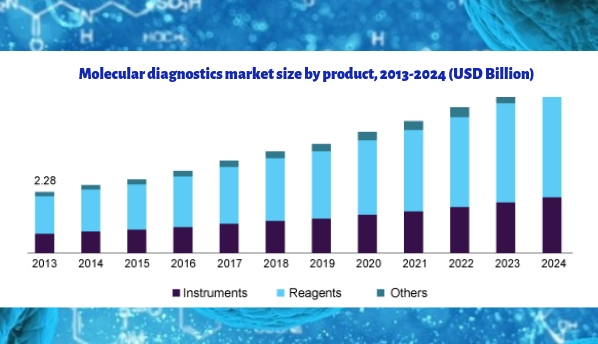
Molecular Diagnostics Market Size, Share & Trend :
Molecular Diagnostics Equipment market is influencing the –
- North America market that contains (United States, Canada, and Mexico),
Molecular Diagnostics Equipment market is growing in -
- Europe market (France, Germany, Italy, UK, and Russia),
witnessed growth in the -
- Asia Pacific region (Japan, China Korea, South East Asia, and India),
followed by Molecular Diagnostics Equipment market in -
- South America (Argentina, Columbia, and Brazil),
and the Middle East and Africa -
- UAE, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, Egypt, and South Africa.
In 2015, the global molecular diagnostics market size was valued at USD 6,451.5 million and is anticipated to grow. In 2018, infectious diseases account for the largest share of the global molecular diagnostics market. Greater accuracy, portability, cost-effectiveness and Technological advancements enable molecular diagnostics to significantly drive the market.
Over the forecast period, the rising prevalence of infectious diseases and hospital-acquired infections are expected to drive market growth. Rise in cardiovascular, neurological, and genetic disorders is also expected to fuel market growth. Governments and different organizations Increase in funding for clinical studies in the molecular diagnosis space boost the market growth.
The hospitals and academic laboratories segment are expected to account for the largest share of the market in 2018.
Why Abu Dhabi, UAE?
The growth of the UAE diagnostic market can be attributed to the high prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases. WHO estimates of all deaths worldwide Chronic diseases account for approximately 60 %. Chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases are responsible for 12%, 40%, 5%, and 5% of mortality in the United Arab Emirates. There has been a paradigm shift from traditional diagnostics to a new generation diagnostic, that works at the gene level. The inclusion of Advanced technologies such as genetic testing, molecular diagnostics, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and next-generation sequencing (NGS) made it possible.
The major market players in the UAE molecular diagnostics market are :
- BioMérieux
- Qiagen
- Abbott Laboratories
- Roche Diagnostics and
- Siemens among others
The competition among manufacturers is increasing, with the increasing number of companies.
Related Conferences :
- International Conference on Molecular Markers and Cancer Therapeutics, October 14-15, 2019 | Abu Dhabi, UAE
- 2nd International Conference on Molecular Biology and Medicine, December 16-17, 2019 | Dubai, UAE
- 2nd Annual Congress on Bacterial, Viral and Infectious Diseases, June 17-18, 2019 | Dubai, UAE
- 9th International Conference on Bacteriology and Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019 | Abu Dhabi, UAE
- 26th Cancer Genomics Congress: New Era for Cancer Prevention, July 15-16, 2019 | Abu Dhabi, UAE
- International Conference on Molecular Markers and Cancer Therapeutics, October 14-15, 2019 | Abu Dhabi, UAE
- International Conference on Biomarkers and Cancer Targets, October 14-15, 2019 | Abu Dhabi, UAE
- International Conference on Biomarkers and Clinical Research, July 15-16, 2019 | Abu Dhabi, UAE
- 3rd Annual Aging Conference: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutics, September 23-24, 2019 | Dubai, UAE
- Cellular and Molecular Mechanism Conference: Health and Disease, November 21-22, 2019 | Bali, Indonesia
- 10th International Conference on Tissue Science and Regenerative Medicine, September 23-24, 2019 | Radisson, Narita | Tokyo, Japan
- International Conference on Genetic Disorders and Gene Therapy, August 30-31, 2019 | Bangkok, Thailand
- 12th World Congress on Cell & Tissue Science, September 13-14, 2019 | Singapore
- 12th Annual Conference on Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, June 13-14, 2019 | Helsinki, Finland
- 5th International Congress on Epigenetics & Chromatin, August 22-23, 2019 | Vienna, Austria
- 11th International Conference on Predictive, Preventive and Personalized Medicine & Molecular Diagnostics, Oct 25-26, 2019 | Vancouver, Canada
- 2nd Annual Biotechnology Congress, July 31-Aug 01, 2019 | Chicago, Illinois, USA
- Annual Congress on CRISPR Cas9 Technology and Genetic Engineering, October 18-19, 2019 | Dallas, USA
- 12th International Conference on Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine, November 11-12, 2019 | Madrid, Spain
Companies related to Molecular Medicine :
- 10X Genomics, Pleasanton, CA, USA
- Agena Bioscience, San Diego, CA, USA
- Ambry Genetics, Aliso Viejo, CA, USA
- Aros Applied Biotechnology, Aarhus, Denmark
- Axeq Technologies, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- Axeq Technologies, Seoul, Korea
- BioSpyder Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA
- BN Products & Services, Pargas, Finland
- Cellectis, Romainville, France
- Color Genomics, Millbrae, CA, USA
- DNA Technology (Biosearch Technologies), Risskov, Denmark
- Empire Genomics, Buffalo, NY
- Equenom, San Diego, CA, USA
- Eton Bioscience, Durham, NC
- GATC Biotech, Constance, Germany
- GATC Biotech, Mulhouse, France
- Genapsys, Redwood City, CA, USA
- Genetic Analysis, As, Norway
- Genetic Technologies Group, Fitzroy, Australia
- Gene Works, Hindmarsh, SA, Australia
- GigaGen, San Francisco, CA, USA
- KeyGene, Wageningen, Netherlands
- Mesa Tech, San Diego, CA, USA
- NeoGenomics, Irvine, CA, USA
- Omixon, Budapest, Hungary
- Pharmozyne, Sunnyvale, CA, USA
- Precision Biomarker Resources, Evanston, IL
- Predictive Biology, Carlsbad, CA, USA
- Real Time Genomics, Hamilton, New Zealand
- Response Genetics, Los Angeles, CA, USA
- Retrogen, San Diego, CA, USA
- SciGenom, San Francisco, CA, USA
- Sciomics, Heidelberg, Germany
- Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan
- ValueGene, San Diego, CA, USA
- Vectalys, Toulouse, France
- WaferGenBiosystems, Fremont, CA, USA
Related Societies and Associations :
- Adult Stem Cell Research Network
- Alliance for cellular signaling
- Alzheimer’s Cure Foundation
- American Academy of Anti-Ageing Medicine (A4m)
- American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
- American Cancer Society
- American Society for Cell Biology
- American Society for Investigating Pathology
- American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ASGCT)
- American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG)
- American Society Radiation Oncology
- Association for studies in computational biology
- Australasian Gene and Cell Therapy Society (AGCTS)
- Australasian Proteomics Society
- Austrian Network for Gene Therapy
- Biotechnology and Biological Research Council
- British Society of Gene Therapy
- European Association of Pharma Biotechnology
- European Federation of Biotechnology
- European molecular biology laboratory
- European Peptide Society
- European Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ESGCT)
- French Society of Cellular and Gene Therapy (SFTCG)
- German Gene Therapy Society (DGGT)
- German Resource Centre for Genome Research
- International Society for Cancer Gene Therapy (ISCGT)
- International Union of Toxicology
- Irish Society for Gene & Cell Therapy (ISGCT)
- Japan Society for Gene Therapy (JSGT)
- The Australian biotechnology association
- The European Association for Bioindustries
- The human genome variation society
- The international centre for genetic engineering and biotechnology
Molecular Automation in Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory - The future of Molecular Diagnosis
Automation poised to disrupt terribly the structure of molecular medicine laboratories. New molecular automation systems are capable of connecting directly to clinical chemistry and immunoassay lines, potentially moving high-volume testing out of molecular diagnostics entirely. Moving nucleic acid testing out of molecular laboratories presents a unique challenge, not just in automation but also in controlling the risk for contamination. There are the kind of issues unique to molecular testing that companies need to consider when designing automation systems. A 10-year experience of automated molecular diagnostic platform carries out 91 different real-time PCR. Progresses and future perspectives in molecular diagnostic microbiology are reviewed. At least for defined clinical settings such as emergencies, and in a novel perspective. It is time now to fully acknowledge the true contribution of molecular diagnostic and to reconsider the indication for PCR, by also using these tests as first-line assays.
Travel tips to visit ABU DHABI🌇
Abu Dhabi is the second largest city of the UAE. Tourists can travel around the city exploring the intriguing archaeological and historic sites, as well as the interesting museums, beautiful parks, glamorous shopping venues and adventurous water sports. This city is a perfect combination of tradition and modernity that welcomes everyone with respect and warm hospitality. Abu Dhabi , a cosmopolitan city which offers extreme nightlife, a wide range of restaurants, cultural and musical events for all ages.
Abu Dhabi city has a calm and relaxed dress code. In summer, lightweight clothing is always advisable. Even though this town is a summer destination, it is necessary to carry warm clothes in winter as temperatures are quite low in the evenings.
Improper dressing ought to be avoided publicly area unit as however swimsuits or short garments are allowed on the beaches. In Arabic Abu Dhabi means 'Father of the Gazelle' As the capital town of the United Arab Emirates, Abu Dhabi has much to offer.
Essential DO'S AND DONT'S when visiting the Abu Dhabi
- Simply can need keep in mind once you visit ensure you stay safe.
- It is NOT as conservative as many of you might think.
- Be Sure to Dress Properly.
- Public display of affection is frowned.
- Alcohol is expensive!
- Beware of materials in your baggage
- Tipping is not mandatory
- Must keep your documents like passport or identity with you
- Do not take drugs with you as it is illegal .
Conference Highlights
- Molecular Medicine
- Molecular Diagnostics
- Molecular Genetics and Genomics
- Molecular Oncology
- Molecular Biomarkers and Diagnosis
- Cellular and Molecular Biology
- Molecular Pathology
- Molecular Evolution
- Advances in Molecular Diagnostics
- Prenatal Molecular Diagnostics
- Point-of-Care Diagnostics
- Clinical Diagnostics & Research
- Infectious Diseases
- Next-Generation Sequencing
- Immunogenicity Testing
- Metagenomics
- Stem Cell & Regeneration
- Clinical Chemistry
- Pharmacogenomics
- DNA sequencing
- Translational and Molecular Medicine
- Integrative Molecular Medicine
- Biosimilar Monoclonal Antibodies
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 15-16, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Molecular Biomarkers & Diagnosis
- Journal of Molecular and Genetic Medicine
- Journal of Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by